React Query enables fetching, caching, synchronizing, and updating server state in React applications. It might sound a lot for some. However, we can take each part from React Query and learn what makes it great.
What is State Management?
For React, State Management is a way to enable communication and sharing of data across components. Let us try to understand the use of state management tools with an example.
Here is a cart page from Amazon.com. Visualize the red boxes as three React components.
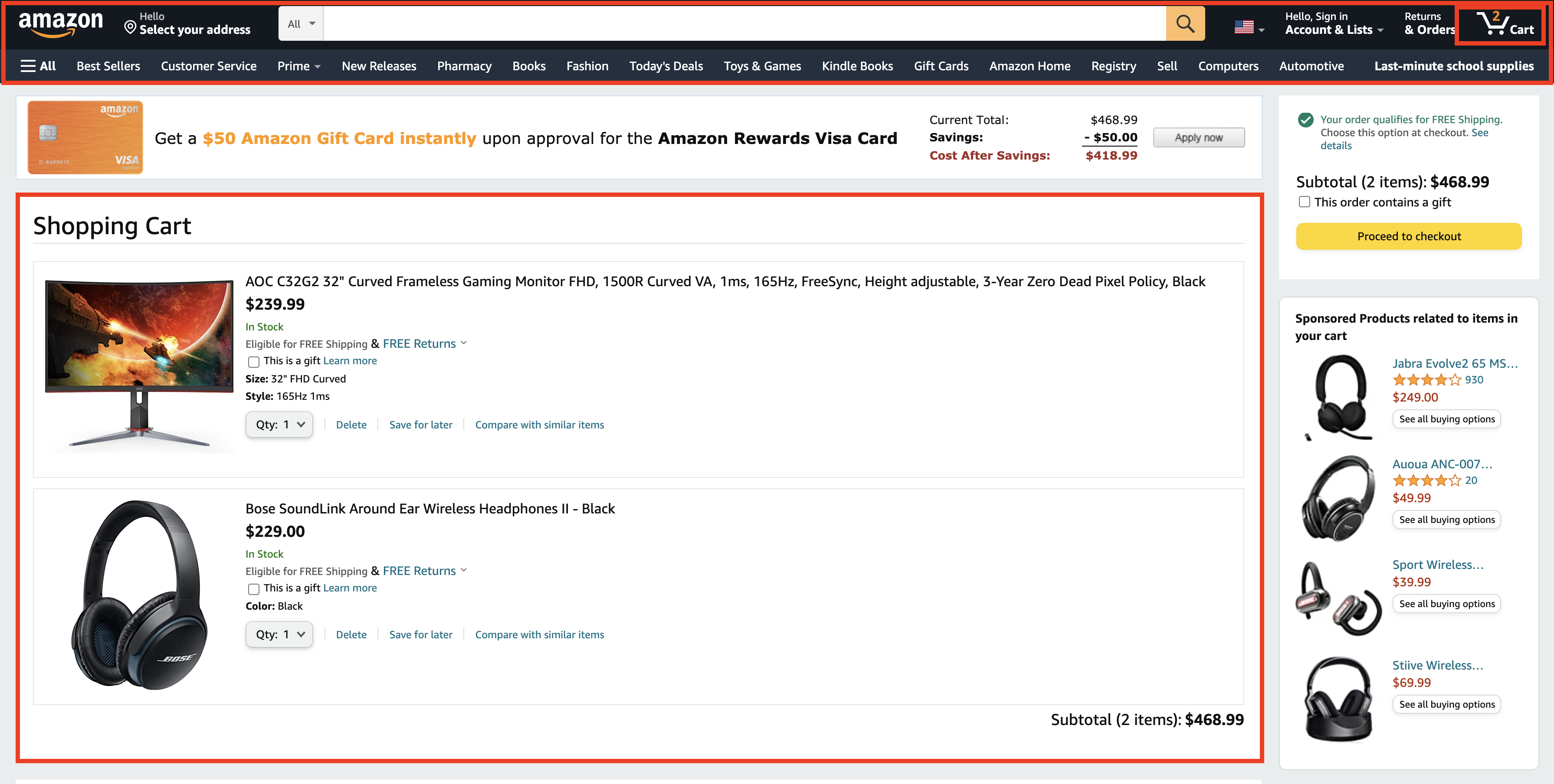
We have a Header component, and inside that, there is a MiniCart component. Then, finally, in the main content area, we have a CartDetails component.
CartDetails component gets the items in the cart from the server. MiniCart component also is waiting for the items in the cart. Then only it can display the count of items. But, since CartDetails and MiniCart are two independent components, they cannot share the data.
A state manager comes to the rescue here. It acts as a global data store. In our case, the CartDetails component can store the cart details in the state manager as soon as it receives the API response. MiniCart, on the other hand, is listening to the state manager for any updates on cart data. Every state manager like Redux, ReCoil, or React Query serves this purpose in their way.
We can imagine the global data store as a JavaScript object. When the cart page loads, the data store looks like this:
{
cart: [];
}Once the CartDetails component fetches the cart details, it updates the global data store like this:
{
cart: [
{
name: 'AOC C32G2 32" Curved Frameless Gaming Monitor FHD, 1500R Curved VA, 1ms, 165Hz, FreeSync, Height adjustable, 3-Year Zero Dead Pixel Policy, Black',
price: "$239.99",
},
{
name: "Bose SoundLink Around Ear Wireless Headphones II - Black",
price: "$229.00",
},
];
}Since the MiniCart component listens to the data store, it can immediately know the number of items in the cart.
Server State vs. Client State
State managers hold the state of a web page. For easy understanding, we are on the registration page of a website. It contains a form to collect user details. Assume that the user filled the complete form, and now the state looks like this:
{
name: "Vicky",
email: "vicky@gmail.com",
isEmailUnique: true,
acceptedTerms: true
}To understand what is server state and client state, we need to ask a question to each field in the data store.
"Is the value of the <key> still <value>?"And then listen to who is answering. E.g. Is the value of the name still Vicky? The client can say "yes" because the name is still there in the client-side registration form. Therefore the name is a client state. The same goes for email.
What about isEmailUnique? Is the value of the isEmailUnique still true? The client cannot tell the answer because it does not know if some other user already registered the email in the meantime. The server can confirm it. Therefore, isEmailUnique is a server state.
Client State Managers With Server State
Redux is a client state manager. React developers store client and server state in Redux store. Let us revisit our Amazon cart page.

When the cart page loads, we call a cart API and stores the response in the Redux store. The CartDetails component takes the cart details from the store and displays the information.
Is there any flaw in the above technique? Yes. As React Redux developers, we are on the assumption that Redux has successfully grasped the server state. But in reality, Redux might be storing stale data. For example, the user might have added one more item through their mobile application. Later, when the user returns to the website to complete the order, they do not see the updated cart.
React Query is a server state manager who can handle server-side state accurately and efficiently.
React Query and Server State
We will understand how React Query and Server State are connected using the same Amazon page mentioned above.
What if we are using React Query instead of Redux? The first main difference is that we do not fetch the API data and give it to React Query. Instead, we give a promise to React Query, which, when resolves, obtain the API response. It is like we are not catching fish and handing it over to React Query. Instead, we are giving our fishing rod so that React Query can catch fish at any time.
React Query fetches the latest data whenever required and keeps the server state synchronous with the client data store.
Summary
State management helps to share data across React components. There are two types of states, client state and server state. When Redux is suitable for the client state, React Query is best for server-side state management.
