Webpack creates a single bundle file including all the source files. If the bundle size is big, it can impact initial page load time. At that time, there is an option to split the bundle to multipe files using Webpack and import() function.
Why Code Splitting?
Before doing code splitting, let us understand why we require it in the first place. Create a folder anywhere in your laptop and initialize a node package using yarn init -y or npm init -y. In order to run yarn command, we need to have yarn installed globally.
Next, create an index.js file under /src folder. Here is the content for that file.
console.log("Page loaded");
document.getElementById("mybtn").addEventListener("click", function () {
console.log("Button Clicked");
console.log("I am going to print number 1");
console.log("I am going to print number 2");
console.log("I am going to print number 3");
console.log("I am going to print number 4");
console.log("I am going to print number 5");
});Above code logs a message on page load. It also logs some messages when a button is clicked. We have added 5 console log statements just to increase file size.
HTML
In order to see the working of above JavaScript code, we need to create a HTML file in /dist folder. We are creating in /dist folder because after webpack build, the bundle file(main.js) is created there.
Create an index.html file in /dist folder and paste below contents:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="mybtn">Click Me!</button>
<script src="./main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>We have a button added to fire the event we wrote in js file. Also, we placed the script tag at the bottom of file to properly attach the button with the click event.
Build
We now have the source files and HTML ready. Now, let us configure webpack to run in development mode. Here is the content for webpack.config.js file.
module.exports = {
mode: "development",
};We can also add a command in package.json to run webpack.
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack"
},Now, go to project folder in terminal and execute yarn build.

A bundle file of size 1.55Kb is created. If we load the HTML in browser and click the button, we can see below output in console.
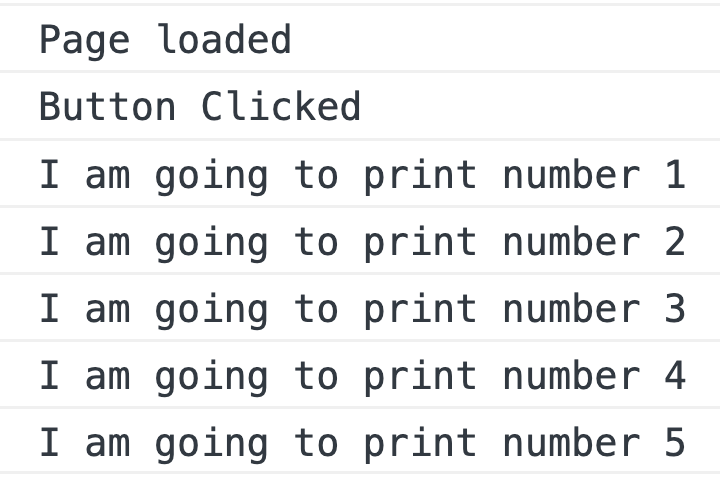
If we analyze what just happened, we are loading the full bundle file of 1.55Kb on page load. That slows initial page load time. We can split the button click logic to a separate file. That can improve the site performance. In the next section, we will see how it is done.
Split JS Code
Let us create a separate file under /src folder called eventHandler.js. We then move all the button click logic to that file.
export default () => {
console.log("Button Clicked");
console.log("I am going to print number 1");
console.log("I am going to print number 2");
console.log("I am going to print number 3");
console.log("I am going to print number 4");
console.log("I am going to print number 5");
};Next, we dynamically import this file in index.js only on button click.
document.getElementById("mybtn").addEventListener("click", function () {
import("./eventHandler").then((mod) => {
mod.default();
});
});When Webpack sees the dynamic import() statement, it automatically extract the logic to a separate bundle file.
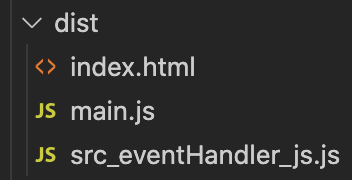
At the time of page load, only the main.js file is loaded. When the button is clicked, Webpack asynchronously request for src_eventHanlder_js.js and executes the click handler logic.
This is how code splitting is done using import() improves web performance. There are other ways also to implement code splitting.
