Webpack creates a bundle file from the source files. In webpack configuration file, there is an option to provide the file name of the output bundle file. If the name is static, then the browser loads the file for the first time from the server. From the second time, it will take the file from browser cache. That will create a problem if bundle file is updated in the server.
In this article, we are trying to find a solution for this caching problem and find out what is the best method to cache.
Project Setup
First step is to initialize a NPM package using npm init -y or yarn init -y.
Second step is to install webpack and webpack-cli as dev dependencies.
yarn add -D webpack webpack-cliAs third step, add a build command under scripts in package.json.
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack"
},Now we are technically ok to try webpack.
Building Source
Create a folder src in our project root. We will store all our source code inside this folder. Create an index.js file inside src folder and fill it with below content.
console.log("Hello World!");Now, take terminal and navigate to our project folder and run:
yarn buildAbove command creates a dist folder and places our bundle(main.js) inside it. Assume, we included this main.js file in our HTML file. When a user first visits the page, main.js is downloaded from server. But when the user visits the page next time, the browser will take main.js from browser cache. That is good. right? But there is a problem.
Content Change
What if we change the text in index.js to "Hello universe!!"? Webpack build followed updated main.js. But our browser is still fetching from its cache. How to solve it?
So far, we did not create a webpack.config.js because we were using the default options of webpack. Now, create a webpack.config.js file. Fill it with below content.
module.exports = {
output: {
filename: "main.[contenthash].js",
},
};[contenthash] acts like a placeholder. Webpack will calculate the hash value of source files included and fill it in [contenthash] placeholder. In our case, when yarn build is run, we can see a file like main.09a3ac0effce240721db.js in dist folder. Again this file will be cached by browser. But, if we make any change to any files and do a build again, the hash value changes. If I change "World" to "Universe" in index.js, I can see that the output bundle file name is now main.ffae18492c7b67357218.js. There is no chance that browser serves the bundle from cache now because the file name itself has changed.
Cleaning Dist Folder
After taking several builds according to new settings, we can see that the dist folder is filling up with lot of bundle files.
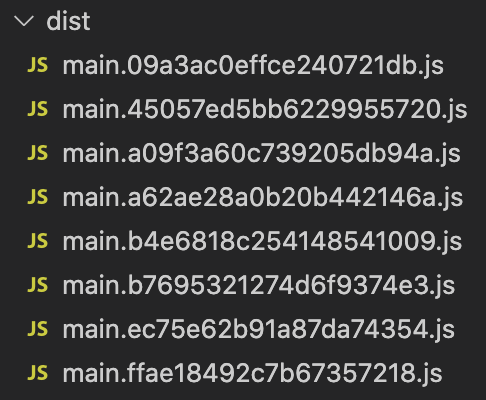
We can easily solve this problem. output configuration in webpack has a clean property. If we set the clean property to true, webpack will clean the dist folder in each build. Here is the updated webpack.config.js file:
module.exports = {
output: {
filename: "main.[contenthash].js",
clean: true, },
};Summary
We learned how to efficiently handle caching in webpack. Using [contenthash] placeholder, we can force browsers to fetch latest and updated bundle file after each build. We can also keep our distribution folder clean using the output.clean property. Have fun!.
